Jan 9, 2012 (GlobeNewswire via COMTEX) --
Once-daily ACH-1625 safe, well-tolerated and achieves 100% cEVR after 12 weeks of treatment
Pilot study of ACH-1625 in HCV genotype 3 achieves maximal 3.68 log10 reduction
ACH-2684 safe, well tolerated and achieves HCV genotype 1 maximal 4.63 log10 reduction; Additional dosing on-going
NEW HAVEN, Conn., Jan. 9, 2012 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. a leader in the discovery and development of small molecule drugs to combat the most challenging infectious diseases, today reported new clinical trial results on its portfolio of protease inhibitors including: Phase 2 interim 12-week treatment results with ACH-1625 for the treatment of genotype 1 treatment-naive hepatitis C virus (HCV), exploratory data on ACH-1625 for the treatment of HCV genotype 3, and initial proof-of-concept data for ACH-2684. Based upon these results, Achillion is planning further exploration of ACH-1625 in combination with other oral antiviral agents for the treatment of all HCV genotypes and continues to evaluate ACH-2684 in a Phase 1 clinical trial.
Michael D. Kishbauch, President and Chief Executive Officer of Achillion commented, "ACH-1625 is emerging as a fascinating and potentially superior, once-daily protease inhibitor that competes well against all other DAAs in development, regardless of their mechanism, based upon ACH-1625's safety, efficacy, genotypic coverage and emerging resistance mutation profile. Further, ACH-2684 shows preliminary promise in its ability to treat HCV, with a safety profile that looks very good, and over the next few months we will expand our clinical experience to define the dose response for its use across all HCV genotypes."
ACH-1625: Phase 2 12-Week Study Design and Interim Results
In the second segment of this ongoing Phase 2a trial, three doses of once-daily ACH-1625 (200 mg, 400 mg or 800 mg) in combination with pegylated interferon alfa-2a and ribavirin (P/R) were dosed over 12 weeks of therapy in patients with treatment-naive HCV genotype 1. Subjects were randomized and stratified by IL28B genotype, including CT and TT, which is a marker of a patient's diminished response to interferon.
Enrollment in this study of approximately 60 patients has been completed, and data on the first 35 patients enrolled were evaluated in this interim analysis. Of the patients enrolled, the majority had HCV genotype 1a (n=23/35 (66%)), with remaining patients having HCV genotype 1b (n=10) or genotype 1 (n=2). Approximately 66% of the patients were IL28B genotype CT/TT, the more difficult to treat mutation, 74% were male and approximately 14% were African American. No viral breakthroughs were observed during treatment. Preliminary results for the first 35 patients enrolled demonstrated rapid virological response (RVR) at week 4, and complete early virologic response (cEVR) and viral load reduction at week 12 as follows:
(Click on pictures to enlarge)

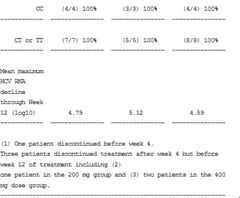
"We were pleased to note that regardless of IL28B status, 100% of patients treated through 12 weeks achieved cEVR and remained undetectable at this point in the study, and the potency and unique pharmacokinetic properties of ACH-1625 appear to provide very potent antiviral coverage for all of these genotype 1 patients," commented Dr. Elizabeth A. Olek, Chief Medical Officer of Achillion. "Patients appear to have continued on-treatment viral suppression, and we therefore look forward to determining end-of-treatment response rates for the fully enrolled study and to presenting complete study results in April."
Safety results from this segment of the trial were similar to those observed in the previously reported clinical trials of ACH-1625. Over 12 weeks of co-administration of ACH-1625 plus P/R, there was one reported serious adverse event (SAE) that was deemed unrelated to ACH-1625. Most reported adverse events (AEs) in patients receiving ACH-1625 were classified as mild to moderate and were transient. The most common AEs were consistent with pegylated interferon alfa-2a and ribavirin treatment.
ACH-1625: Pilot Phase 1 Study Evaluating Antiviral Activity against HCV Genotype 3 and Clinical Virology Assessment of HCV Genotype 1
Based upon in vitro virology, as well as evolving clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data, a Phase 1 pilot study was conducted to evaluate the antiviral activity of ACH-1625 for the treatment of HCV genotype 3. A total of seven patients infected with HCV genotype 3 were enrolled and treated with monotherapy consisting of 400 mg ACH-1625 twice daily for 4.5 days. In this exploratory study, ACH-1625 was safe and well tolerated. The maximum HCV genotype 3 RNA viral load reduction achieved was 3.68 log10 among the six out of seven patients that achieved an antiviral response.
In addition, clinical virology analysis of patient samples obtained during the first Phase 2 28-day study segment of ACH-1625 in combination with P/R examined the resistance mutation profile following treatment. The results indicated that following 28 days of treatment with ACH-1625 the presence of highly resistant variants were not detected.
"These findings suggest that ACH-1625 maintains high concentrations in the liver, the site of infection, resulting in a unique pharmacokinetic drug profile. These positive clinical results in genotype 3, along with the strong virologic profile of ACH-1625, have led us to take a broad look at the role of ACH-1625 in our future proprietary combination regimen," commented Milind Deshpande, Ph.D., President of Research and Development and Chief Scientific Officer.
ACH-2684: Phase 1 Healthy Volunteers and HCV Genotype 1 and 3 Segments
This Phase 1 clinical study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic profile and antiviral activity of ACH-2684. Healthy volunteers in the single ascending dose (SAD) segment received doses of ACH-2684 ranging from 10 mg once daily to 300 mg twice daily. The first cohorts of HCV-infected patients were enrolled and treated with ACH-2684 administered as 400 mg twice daily for 2.5 days.
ACH-2684 was well tolerated at all doses and there were no serious adverse events, no clinically significant changes in vital signs, ECGs, or laboratory evaluations. All reported adverse events were classified as mild or moderate, were transient and showed no apparent dose relationship.
Proof-of-concept was achieved with ACH-2684 in HCV genotype 1 demonstrating a maximum HCV RNA viral load reduction of 4.63 log10. Antiviral activity with ACH-2684 in HCV genotype 3 was seen with a maximum HCV RVA viral load reduction of 2.03 log10. Additional cohorts of patients with either HCV genotype 1 or HCV genotype 3 are currently being enrolled to further explore doses and viral kinetics for ACH-2684.
All-Oral Protease Inhibitor and NS5A Inhibitor Combination Will Play an Important Role
During 2012 Achillion plans to conduct a number of clinical trials to further characterize its portfolio of protease inhibitors, including ACH-1625 and ACH-2684, and its NS5A inhibitors, including ACH-2928 and ACH-3102. In addition to the ongoing Phase 1 trials with ACH-2684 and ACH-2928, Achillion plans to submit an investigational new drug (IND) application and initiate a Phase 1 clinical trial with ACH-3102 during the second quarter of 2012. During the second half of 2012, Achillion plans to initiate an all-oral interferon-free combination study which will evaluate a protease inhibitor and a NS5A inhibitor, with or without ribavirin, for the treatment of HCV.
"We believe that the protease and NS5A inhibitor combination will play an important role in the future treatment of HCV across all genotypes," commented Mr. Kishbauch. "With the robust portfolio we have discovered and developed here at Achillion, we believe we are uniquely positioned to advance a potentially best-in-class all-oral, interferon-free combination and are looking forward to initiating clinical development with this regimen later in the year."
About ACH-1625
ACH-1625 is a pan-genotypic HCV protease inhibitor designed and synthesized based on crystal structures of enzyme/inhibitor complex. ACH-1625 is an open chain, non-covalent, reversible inhibitor of NS3 protease. In preclinical studies, ACH-1625 demonstrated high potency, unique pharmacokinetic properties and an excellent safety profile at high drug exposures. ACH-1625 has rapid and extensive partitioning to the liver, as well as high liver/plasma ratios. ACH-1625 has shown low single-digit nanomolar potency that is specific to HCV. It is equipotent against HCV genotypes 1a and 1b at IC50 of approximately 1nM. ACH-1625 is currently in a Phase 2 clinical trial and has shown clinical antiviral activity against genotypes 1 and 3. Fast Track status was granted to ACH-1625 in 2012 for the treatment of chronic HCV.
About ACH-2684
ACH-2684 is a next-generation HCV protease inhibitor designed and synthesized based on crystal structures of enzyme/inhibitor complex. ACH-2684 is a macro-cyclic, non-covalent, reversible inhibitor of NS3 protease. In preclinical studies, ACH-2684 demonstrated pico-molar potency, excellent pharmacokinetic properties and safety profile at high drug exposures. ACH-2684 also exhibits rapid and extensive partitioning to the liver, as well as high liver/plasma ratios in preclinical studies. ACH-2684 has shown pico-molar potency against NS3 protease that is specific to HCV. It has preclinical activity against the 6 known genotypes of HCV and exhibits equipotent activity against HCV genotypes 1a and 1b at an IC50 of approximately 100 pico-molar. The drug candidate was discovered internally and is being advanced by Achillion.
About HCV
The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of viral hepatitis, which is an inflammation of the liver. It is currently estimated that more than 170 million people are infected with HCV worldwide including nearly 4 million people in the United States, more than twice as widespread as HIV. Three-fourths of the HCV patient population is undiagnosed; it is a silent epidemic and a major global health threat. Chronic hepatitis, if left untreated, can lead to permanent liver damage that can result in the development of liver cancer, liver failure or death. Few therapeutic options currently exist for the treatment of HCV infection. The current standard of care is limited by its specificity for certain types of HCV, significant side-effect profile, and injectable route of administration.
About Achillion Pharmaceuticals
Achillion is an innovative pharmaceutical company dedicated to bringing important new treatments to patients with infectious disease. Achillion's proven discovery and development teams have advanced multiple product candidates with novel mechanisms of action. Achillion is focused on solutions for the most challenging problems in infectious disease including hepatitis C and resistant bacterial infections. For more information on Achillion Pharmaceuticals, please visit www.achillion.com or call 1-203-624-7000.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 that are subject to risks, uncertainties and other important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those indicated by such forward-looking statements, including statements with respect to: the potency, safety, tolerability, effectiveness and other characteristics of Achillion's protease inhibitors and NS5A inhibitors; Achillion's expectations regarding timing for the commencement, completion and reporting of results of clinical trials of drug candidates in its protease inhibitor and NS5A inhibitor programs; the potential for its protease and NS5A inhibitor combination to play an important role in the future treatment of HCV across all genotypes; and Achillion's ability to advance a potentially best-in-class all-oral, interferon-free combination protease and NS5A inhibitor. Among the factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those indicated by such forward-looking statements are risks relating to, among other things Achillion's ability to: replicate in later clinical trials positive results found in earlier stage clinical trials of ACH-1625, ACH-2684 and its other product candidates; advance the development of its drug candidates under the timelines it anticipates in current and future clinical trials; obtain necessary regulatory approvals; obtain patent protection for its drug candidates, and the freedom to operate under third party intellectual property; establish commercial manufacturing arrangements; identify, enter into and maintain collaboration agreements with appropriate third-parties; compete successfully with other companies that are seeking to develop improved therapies for the treatment of HCV; and raise the substantial additional capital needed to achieve its business objectives. These and other risks are described in the reports filed by Achillion with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, including its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 and its subsequent SEC filings.
In addition, any forward-looking statement in this press release represents Achillion's views only as of the date of this press release and should not be relied upon as representing its views as of any subsequent date. Achillion disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statement, except as required by applicable law.
This news release was distributed by GlobeNewswire, www.globenewswire.com
SOURCE: Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Source








